Build Trust and Protect Your Brand with the Solutions from Top Cybersecurity Brands
Internet protection for you and your customers
Why Choose BoostSSL for Security?
We’re committed to keeping the web safe for all users.
When you buy an SSL certificate from BoostSSL, you get a free site seal, 99% browser ubiquity, and all the data protection your customers demand.
Our SSL products range from basic to advanced, from single- to multi-domain. We have security solutions to fit every business and every budget.
You get top-notch Two-Factor Authentication (U2F & TOTP) to keep your account secure, as well as domain privacy protection - all free of charge.
Every BoostSSL product is backed by our rock-solid guarantee and friendly, knowledgeable 24/7 support team. Our vast Knowledgebase is also loaded with good information and available anytime.
With NordVPN service, you can change your virtual location to unlock the internet for secure and fast streaming, transferring data, and online gaming.
Work safe no matter your location or device with NordVPN service. Avoid leaking of information about your browsing activity.
Creating a Secure Connection
Invisible to the end-user, a process called the “TLS/SSL handshake” creates a protected connection between your web server and web browser nearly instantaneously every time you visit a website.
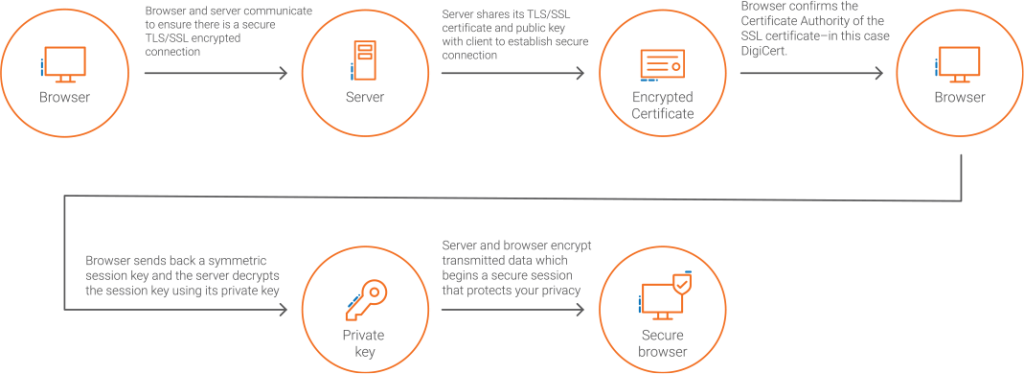

Securing Your Data in Transit and Brand Identity
Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates, also known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are essential to protecting internet browser connections and transactions. They ensure that your website displays a secure message, and that the identity of the domain owner is verified. TLS/SSL is the standard security technology that works behind the scenes to keep your online transactions and logins secure—here is how it works.





